Terms and acronyms
| Terms | Details |
| DMA | Direct Memory Access. For an introduction to DMA, please refer to DMA in Wikipedia. |
| GPIO | General Purpose Inputs-Outputs. For more details, please refer to the GPIO module in HAL. |
| I2C | Inter-Integrated Circuit. I2C is typically used to attach low-speed peripheral ICs to processors and microcontrollers. For an introduction to I2C, please refer to I2C in Wikipedia. |
| NVIC | Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller. NVIC is the interrupt controller of ARM Cortex-M4. For more details, please refer to NVIC introduction in ARM Cortex-M4 Processor Technical Reference Manual. |
Supported features
Software architecture of the I2C
- Polling mode architecture.
Polling mode architecture is similar to the polling mode architecture in HAL overview. See HAL Driver Model for polling mode architecture.
- DMA mode architecture.
DMA mode architecture is similar to the interrupt mode architecture in HAL overview. See HAL Driver Model for interrupt mode architecture.
How to use this driver
- Using I2C in polling mode.
To use I2C driver in a polling mode, configure GPIO pins to pinmux to SCL and SDA, then call hal_pinmux_set_function() to select the pinmux function. After setting the pinmux, call hal_i2c_master_get_running_status() to check the I2C status. If the status is HAL_I2C_STATUS_BUS_BUSY, wait till the status becomes HAL_I2C_STATUS_IDLE. Once the data is successfully transmitted, call hal_i2c_master_deinit() to release the I2C resource for other users.
Steps are shown below:
- Step1: Call hal_gpio_init() to initialize the pin. For mode details about hal_gpio_init please refer to GPIO module in HAL.
- Step2: Call hal_pinmux_set_function() to set the GPIO pinmux or use the EPT tool to apply the pinmux settings.
- Step3: Call hal_i2c_master_init() to initialize the I2C master.
- Step4: Call hal_i2c_master_send_polling() to send data in a polling mode.
- Step5: Call hal_i2c_master_receive_polling() to receive data in a polling mode.
- Step6: Call hal_i2c_master_deinit() to de-allocate the I2C master if it is no longer in use.
- Sample code:
uint8_t slave_address = 0X50;
const uint8_t send_data[8] = {0x00, 0x00, 0xFF, 0xAA, 0x14, 0x15, 0x16, 0x17, 0x18, 0x19};
uint8_t receive_data[8] = {0};
volatile uint32_t size = 8;
}
}
} else {
}
- Using I2C in DMA mode.
To use I2C driver in DMA mode, configure GPIO pins to pinmux to SCL and SDA, then call hal_pinmux_set_function to select the pinmux function. After setting the pinmux, call hal_i2c_master_get_running_status() to check the I2C status. If the status is HAL_I2C_STATUS_BUS_BUSY, user should wait till the status is HAL_I2C_STATUS_IDLE, then call hal_i2c_master_register_callback() to register a callback function. Once the data transaction is complete, call hal_i2c_master_deinit() in your callback function registered by hal_i2c_master_register_callback() to release the I2C resource to other users. Steps are shown below:
Transaction Length And transaction packet of APIs
The Transaction packet is the transaction packet sent by the I2C master using SCL and SDA. Different APIs have different transaction packets, as shown below.
- Transaction length supported by the APIs
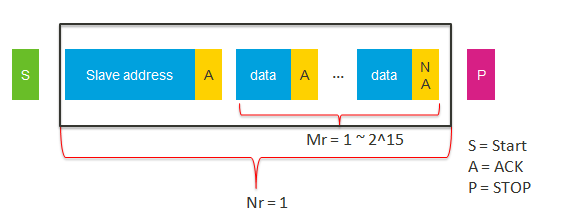
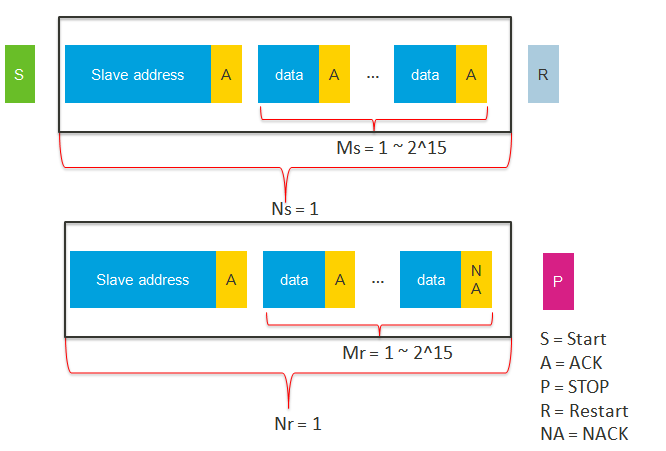
The total transaction length is determined by 4 parameters:
send_packet_length(Ns), which indicates the counts of send packet.
send_bytes_in_one_packet(Ms).
receive_packet_length(Nr).
receive_bytes_in_one_packet(Mr).
And also, these 4 parameters will affect the transaction packet. The ralationship between transaction packet and these 4 parameters will be introduced in the next section.
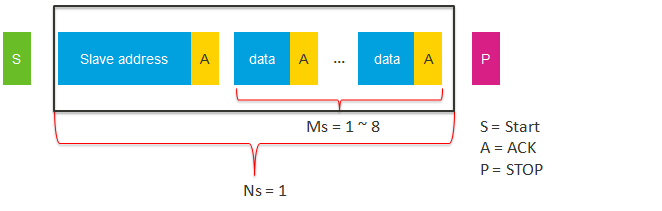
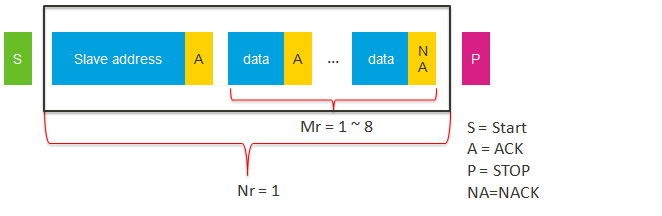
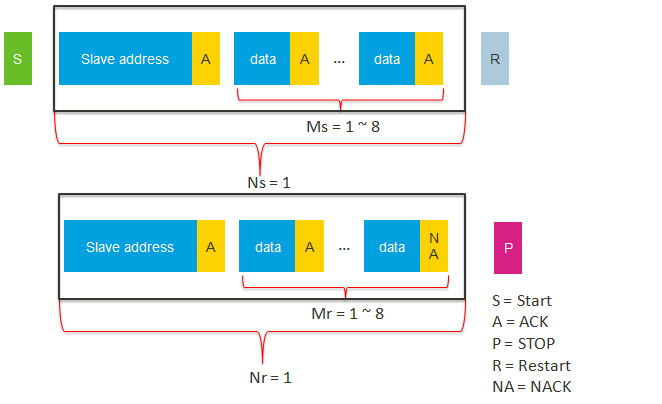
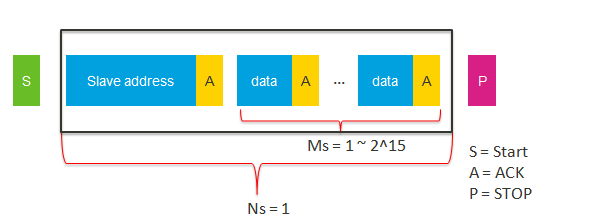
- Total transaction length = Ns * Ms + Nr * Mr.
- Ns is the packet length to be sent by the I2C master.
- Ms is the total number of bytes in a sent packet.
- Nr is the packet length to be received by the I2C master.
- Mr is the total number of bytes in a received packet.
- NA means the related parameter should be ignored.
- 1~8 specifies the parameter range is from 1 to 8. 1~15 specifies the parameter range is from 1 to 15. 1~255 specifies the parameter range from 1 to 255.
- 1 means the parameter value can only be 1.
- Note: Only those functions with the suffix "_ex" have these 4 parameters. Other functions only have the "size" parameter and the driver splits the "size" into these 4 parameters. hal_i2c_master_send_polling() for example, the "size" will be divided like this: send_packet_length = 1, send_bytes_in_one_packet = size. As a result, the total size should be: send_packet_length * send_bytes_in_one_packet = 1 * size = size. The range of "size" should be from 1 to 8.
| API | send_packet_length(Ns) | send_bytes_in_one_packet(Ms) | receive_packet_length(Nr) | receive_bytes_in_one_packet(Mr) |
| hal_i2c_master_send_polling | 1 | 1~8 | NA | NA |
| hal_i2c_master_receive_polling | NA | NA | 1 | 1~8 |
| hal_i2c_master_send_to_receive_polling | 1 | 1~8 | 1 | 1~8 |
| hal_i2c_master_send_dma | 1 | 1~2^15 | NA | NA |
| hal_i2c_master_receive_dma | NA | NA | 1 | 1~2^15 |
| hal_i2c_master_send_to_receive_dma | 1 | 1~2^15 | 1 | 1~2^15 |
- Waveform pattern supported by the APIs
The 4 parameters(send_packet_length(Ns), send_bytes_in_one_packet(Ms), receive_packet_length(Nr), receive_bytes_in_one_packet(Mr) will also affect the transaction packet. The relationship between transaction packet and these 4 parameters is shown below.
- Ns is the send_packet_length.
- Ms is the send_bytes_in_one_packet.
- Nr is the receive_packet_length.
- Mr is the receive_bytes_in_one_packet.
| API | transaction packet format |
| hal_i2c_master_send_polling |
|
| hal_i2c_master_receive_polling |
|
| hal_i2c_master_send_to_receive_polling |
|
| hal_i2c_master_send_dma |
|
| hal_i2c_master_receive_dma |
|
| hal_i2c_master_send_to_receive_dma |
|
|
| hal_i2c_status_t | hal_i2c_master_init (hal_i2c_port_t i2c_port, hal_i2c_config_t *i2c_config) |
| | This function initializes the I2C master before starting a transaction. More...
|
| |
| hal_i2c_status_t | hal_i2c_master_deinit (hal_i2c_port_t i2c_port) |
| | This function releases the I2C master after the transaction is over. More...
|
| |
| hal_i2c_status_t | hal_i2c_master_set_frequency (hal_i2c_port_t i2c_port, hal_i2c_frequency_t frequency) |
| | This function sets the transaction speed. More...
|
| |
| hal_i2c_status_t | hal_i2c_master_register_callback (hal_i2c_port_t i2c_port, hal_i2c_callback_t i2c_callback, void *user_data) |
| | This function registers a callback function while using DMA mode. More...
|
| |
| hal_i2c_status_t | hal_i2c_master_send_polling (hal_i2c_port_t i2c_port, uint8_t slave_address, const uint8_t *data, uint32_t size) |
| | This function sends data to I2C slave in polling mode. More...
|
| |
| hal_i2c_status_t | hal_i2c_master_send_dma (hal_i2c_port_t i2c_port, uint8_t slave_address, const uint8_t *data, uint32_t size) |
| | This function sends data to I2C slave in DMA mode. More...
|
| |
| hal_i2c_status_t | hal_i2c_master_receive_polling (hal_i2c_port_t i2c_port, uint8_t slave_address, uint8_t *buffer, uint32_t size) |
| | This function receives data from I2C slave in a polling mode. More...
|
| |
| hal_i2c_status_t | hal_i2c_master_receive_dma (hal_i2c_port_t i2c_port, uint8_t slave_address, uint8_t *buffer, uint32_t size) |
| | This function receives data from I2C slave in a DMA mode. More...
|
| |
| hal_i2c_status_t | hal_i2c_master_send_to_receive_polling (hal_i2c_port_t i2c_port, hal_i2c_send_to_receive_config_t *i2c_send_to_receive_config) |
| | This function sends data to and then receives data from I2C slave in a polling mode. More...
|
| |
| hal_i2c_status_t | hal_i2c_master_send_to_receive_dma (hal_i2c_port_t i2c_port, hal_i2c_send_to_receive_config_t *i2c_send_to_receive_config) |
| | This function sends data to and then receives data from I2C slave in a DMA mode. More...
|
| |
| hal_i2c_status_t | hal_i2c_master_get_running_status (hal_i2c_port_t i2c_port, hal_i2c_running_status_t *running_status) |
| | This function gets running status of the I2C master. More...
|
| |
This function releases the I2C master after the transaction is over.
Call this function, if the I2C is no longer in use.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | i2c_port | is the I2C master port number. The value is defined in hal_i2c_port_t. |
- Returns
- HAL_I2C_STATUS_INVALID_PORT_NUMBER, an invalid port number is given;
HAL_I2C_STATUS_OK, the operation completed successfully.
- Note
- This function must be called when the I2C is no longer in use, release the I2C resource for the other users to use this I2C master.
- Example
- Sample code, please refer to How to use this driver
- See also
- hal_i2c_master_init()
This function gets running status of the I2C master.
Call this function to check if the I2C is idle or not before transferring data. If it's not idle, then the resource is currently in use, delay the operation until the I2C is idle.
- Parameters
-
- Returns
- HAL_I2C_STATUS_INVALID_PORT_NUMBER, an invalid port number is given;
HAL_I2C_STATUS_OK, the operation completed successfully.
- Example
- Sample code, please refer to How to use this driver
This function initializes the I2C master before starting a transaction.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | i2c_port | is the I2C master port number. The value is defined in hal_i2c_port_t. |
| [in] | i2c_config | Is the configuration parameter to initialize the I2C. Details are described at hal_i2c_config_t. |
- Returns
- HAL_I2C_STATUS_INVALID_PORT_NUMBER, an invalid port number is given;
HAL_I2C_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER, an invalid transfer_frequency is given;
HAL_I2C_STATUS_OK, the operation completed successfully. HAL_I2C_STATUS_ERROR_BUSY, the I2C bus is in use.
- Note
- hal_i2c_master_deinit() must be called when the I2C is no longer in use, release the I2C resource for the other users to use this I2C master. Please DO NOT call hal_i2c_master_init() in interrupt handler, it may cause deadlock. In a multi-task applications, if hal_i2c_master_init() returns error HAL_I2C_STATUS_ERROR_BUSY, it is suggested to call functions that can yield CPU and try again later.
- Example
1 hal_i2c_status_t i2c_master_init(void)
3 hal_i2c_port_t i2c_port;
4 hal_i2c_config_t i2c_config;
5 hal_i2c_status_t error_status;
7 uint32_t try_times = 0;
9 i2c_port = HAL_I2C_MASTER_0;
10 i2c_config.frequency = HAL_I2C_FREQUENCY_400K;
12 while (try_times < 10) {
13 error_status = hal_i2c_master_init(i2c_port, &i2c_config);
14 if (error_status == HAL_I2C_STATUS_ERROR_BUSY) {
15 vTaskDelay((portTickType)100 / portTICK_RATE_MS);
- See also
- hal_i2c_master_deinit()
This function registers a callback function while using DMA mode.
The callback function will be called at I2C ISR routine after the I2C triggers an interrupt. Always call this function to register a callback function while using DMA mode. Refer to Software architecture of the I2C for DMA architecture.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | i2c_port | is the I2C master port number. The value is defined in hal_i2c_port_t. |
| [in] | i2c_callback | is the user-defined callback function called at I2C ISR routine. |
| [in] | user_data | is a user-defined input data returned during the callback function's call. See the last parameter of hal_i2c_callback_t. |
- Returns
- HAL_I2C_STATUS_INVALID_PORT_NUMBER, an invalid port number is given;
HAL_I2C_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER, a NULL function pointer is given by user;
HAL_I2C_STATUS_OK,the operation completed successfully.
- Example
- Sample code, please refer to How to use this driver
This function sends data to and then receives data from I2C slave in a DMA mode.
This function returns immediately after configuring the hardware registers. For more details of DMA mode, see DMA mode in Supported features chapter. For details about transaction length and transaction waveform pattern, see Transaction Length And transaction packet of APIs chapter. Note, not all masters support DMA mode. For more details about DMA mode, see DMA mode of hal_i2c_port_t.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | i2c_port | is the I2C master port number. The value is defined in hal_i2c_port_t. |
| [in,out] | i2c_send_to_receive_config | is the configuration parameter for this API for both send and receive. |
- Returns
- HAL_I2C_STATUS_INVALID_PORT_NUMBER, an invalid port number is given;
HAL_I2C_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER, a NULL buffer pointer is given by user;
HAL_I2C_STATUS_OK, the operation completed successfully;
HAL_I2C_STATUS_ERROR_BUSY, the I2C bus is in use.
- Example
- Sample code, please refer to How to use this driver
- See also
- hal_i2c_master_send_to_receive_polling()