This section introduces the Serial Port Service APIs including terms and acronyms, supported features, software architecture, details on how to use this module, enums, structures and functions.
More...
This section introduces the Serial Port Service APIs including terms and acronyms, supported features, software architecture, details on how to use this module, enums, structures and functions.
The Serial Port Service APIs can be applied to either UART or USB interface. User can easily switch between different devices to match the board configuration through ATCI commands.
Terms and acronyms
| Terms | Details |
| ATCI | AT command interface. For more details about the AT command, please refer to Hayes command set in Wikipedia. |
| NVDM | Non-volatile Data Management is a middleware used to store user data. |
| UART | Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter is usually an individual (or part of an) integrated circuit (IC) used for serial communications over a micro-controller unit (MCU) or peripheral device serial port. For an introduction to UART, please refer to UART in Wikipedia. |
| USB | Universal Serial Bus. USB was designed to standardize the connection of computer peripherals (including keyboards, pointing devices, digital cameras, printers, portable media players, disk drives and network adapters) to personal computers, both to communicate and to supply electric power. It has become commonplace on other devices, such as smartphones, PDAs and video game consoles. USB has effectively replaced a variety of earlier interfaces, such as serial and parallel ports, as well as separate power chargers for portable devices. For more information, please refer to an introduction to the USB in Wikipedia. |
| OP | Operation. |
Supported features
- Supported Serial Port Service AT command format
The command format should start with "AT+EPORT=<OP>", and finish with "<\r><\n>" to mark the end of the AT command. The Serial Port Service module AT command's format is "AT+EPORT=<OP>[,<owner_name>,<device_id>,<param1>,<param2>]".
- <OP> field description
<OP> field has an integer value, each value is described below.
- 0: Display the port assignment for application or user, for example, "ATCI = 1" means the ATCI is using port 1.
- 1: Set a specific port for a specific application or user.
- 2: Switch old port to specific port for the specific application or user at runtime.
- 3: Modify the settings of the devices in Serial Port Service.
- 4: Show the settings of the devices in Serial Port Service.
- <owner_name> field description
<owner_name> field has a string value for application name of Serial Port Service, details are shown below.
- atci: ATCI application.
- syslog: Syslog application.
- <device_id> field description
<device_id> field has an integer value. For more details about each value, please refer to serial_port_dev_t.
- <param1> field description
<param1> field values are described below.
- When <OP>=3 and <device_id>=0/1/2/3, it indicates baudrate of the UART port.
- <param2> field description
<param2> field values are described below.
- When <OP>=0, it indicates the port assignment of applications or users.
- When <OP>=4, it indicates all settings of Serial Port Service devices.
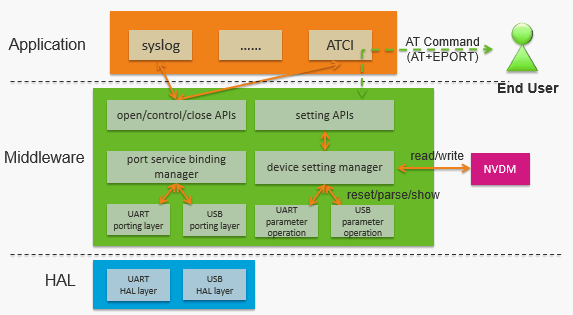
Port_Service architecture
The software architecture is shown in the figure below.
How to use this module
- Step 1. Call serial_port_open() to assign the callback function and open the port.
- Step 2. Call serial_port_control() to read data or write data with a specific command.
- Step 3. Call serial_port_close() to close the serial port if the Serial Port Service is no longer in use.
- Sample code
uint32_t g_serial_port_handle = 0;
uint8_t buffer[8] = {0};
uint8_t buffer_len = 8;
serial_port_open_para.
callback = user_callback;
read_data.
buffer = (uint8_t*) buffer;
read_data.
size = buffer_len;
write_data.
data = buffer;
write_data.
size = buffer_len;
|
| serial_port_status_t | serial_port_open (serial_port_dev_t device, serial_port_open_para_t *para, serial_port_handle_t *handle) |
| | This function initializes the specific device such as UART or USB. More...
|
| |
| serial_port_status_t | serial_port_control (serial_port_handle_t handle, serial_port_ctrl_cmd_t command, serial_port_ctrl_para_t *para) |
| | This function controls a specific device to read or write data or perform other operations supported by the device. More...
|
| |
| serial_port_status_t | serial_port_close (serial_port_handle_t handle) |
| | This function de-initializes a specific device after using the device to release the resources for other users. More...
|
| |
| serial_port_type_t | serial_port_get_device_type (serial_port_dev_t device) |
| | This function gets the device type of the serial port device. More...
|
| |
| serial_port_status_t | serial_port_config_dump_dev_number (uint32_t *user_count, serial_port_assign_t *port_assign) |
| | This function dumps device assign list in NVDM, for example, device UART port0 is assigned to user ATCI. More...
|
| |
| serial_port_status_t | serial_port_config_read_dev_number (const char *user_name, serial_port_dev_t *device) |
| | This function reads assigned device for a specific user. More...
|
| |
| serial_port_status_t | serial_port_config_write_dev_number (const char *user_name, serial_port_dev_t device) |
| | This function writes new assigned device for a specific user. More...
|
| |
| serial_port_status_t | serial_port_config_read_dev_setting (serial_port_dev_t device, serial_port_dev_setting_t *dev_setting) |
| | This function reads current parameters for a specific device. More...
|
| |
| serial_port_status_t | serial_port_config_write_dev_setting (serial_port_dev_t device, serial_port_dev_setting_t *dev_setting) |
| | This function writes new parameters for a specific device. More...
|
| |
This function dumps device assign list in NVDM, for example, device UART port0 is assigned to user ATCI.
Apply this API to identify the user for each device.
- Parameters
-
| [in,out] | user_count | specifies the count of the buffer space pointed to by #port_assign. Upon the return of this function, the value in this parameter means the actual count of the buffer space being used. |
| [out] | port_assign | the serial port assigned to the user. |
- Returns
- SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_FAIL, the function has failed.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_OK, the operation completed successfully.
- Example
2 serial_port_assign_t serial_port_assign[SERIAL_PORT_DEV_MAX];
3 serial_port_status_t status;
4 status = serial_port_config_dump_dev_number(&user_count, serial_port_assign);
5 if (status != SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_OK)
This function reads assigned device for a specific user.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | user_name | is an identifier for the user. |
| [out] | device | is the assigned device for the input user. |
- Returns
- SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER, an invalid parameter error.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_FAIL, the function has failed.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_OK, the operation completed successfully.
- Example
1 serial_port_dev_t syslog_port;
2 serial_port_status_t status;
3 status = serial_port_config_read_dev_number("syslog", &syslog_port);
4 if (status != SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_OK)
This function reads current parameters for a specific device.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | device | is the device to read its current parameters. |
| [out] | dev_setting | is the current parameters for the input device. |
- Returns
- SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER, an invalid parameter error.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_OK, the operation completed successfully.
- Example
1 serial_port_dev_t device;
2 serial_port_status_t status;
3 serial_port_dev_setting_t dev_setting;
4 status = serial_port_config_read_dev_setting(device, &dev_setting);
5 if (status != SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_OK)
This function writes new assigned device for a specific user.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | user_name | is an identifier for the user. |
| [out] | device | is the assigned device for the input user. |
- Returns
- SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER, an invalid parameter error.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_FAIL, the function has failed.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_OK, the operation completed successfully.
- Example
1 serial_port_dev_t syslog_port;
2 serial_port_status_t status;
3 syslog_port = SERIAL_PORT_DEV_USB_COM2;
4 status = serial_port_config_write_dev_number("syslog", syslog_port);
5 if (status != SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_OK)
This function writes new parameters for a specific device.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | device | is the device to write its new parameters. |
| [in] | dev_setting | is the new parameters for the input device. |
- Returns
- SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER, an invalid parameter error.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_OK, the operation completed successfully.
- Example
1 serial_port_dev_t device;
2 serial_port_status_t status;
3 serial_port_dev_setting_t dev_setting;
4 status = serial_port_config_read_dev_setting(device, &dev_setting);
5 if (status != SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_OK)
7 status = serial_port_config_write_dev_setting(device, &dev_setting);
8 if (status != SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_OK)
This function controls a specific device to read or write data or perform other operations supported by the device.
This API must be called after serial_port_open(). User should specify the device with serial port handle. User must also define its callback to handle events reported by the Serial Port Service.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | handle | is the serial port handle for the Serial Port Service. |
| [in] | command | is the command corresponding to a specific parameter. For more details about this parameter, please refer to serial_port_ctrl_cmd_t. |
| [in] | para | specifies the parameter corresponding to a specific command. |
- Returns
- SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER, an invalid parameter error.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_UNINITIALIZED, the serial port device is uninitialized.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_BUSY, the port is busy.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_UNSUPPORTED, the port is not supported.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_OK, the control operation completed successfully.
- Example
1 Sample code, please refer to @ref Port_Service_Usage_Chapter.
This function gets the device type of the serial port device.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | device | is the Serial Port Service device. |
- Returns
- SERIAL_PORT_TYPE_UART, the Serial Port Service device type is UART.
SERIAL_PORT_TYPE_USB, the Serial Port Service device type is USB.
- Example
1 serial_port_type_t device_type;
2 device_type = serial_port_get_device_type(device);
This function initializes the specific device such as UART or USB.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | device | is the Serial Port Service device. For more details about this parameter, please refer to serial_port_dev_t. |
| [in] | para | specifies the callback function. It cannot be NULL. |
| [out] | handle | is the serial port handle for the Serial Port Service. |
- Returns
- SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_INVALID_DEVICE, an invalid device error.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER, an invalid parameter error.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_BUSY, the port is busy.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_UNSUPPORTED, the port is not supported.
SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_OK, the initialization completed successfully.
- Example
1 serial_port_status_t status;
2 uint32_t g_serial_port_handle = 0;
3 serial_port_open_para_t serial_port_open_para;
4 serial_port_open_para.callback = user_callback;
5 status = serial_port_open(port, &serial_port_open_para, &g_serial_port_handle);
6 if (status != SERIAL_PORT_STATUS_OK)
1 void user_callback (serial_port_dev_t device, serial_port_callback_event_t event, void *parameter)
3 // User code to handle the serial port event